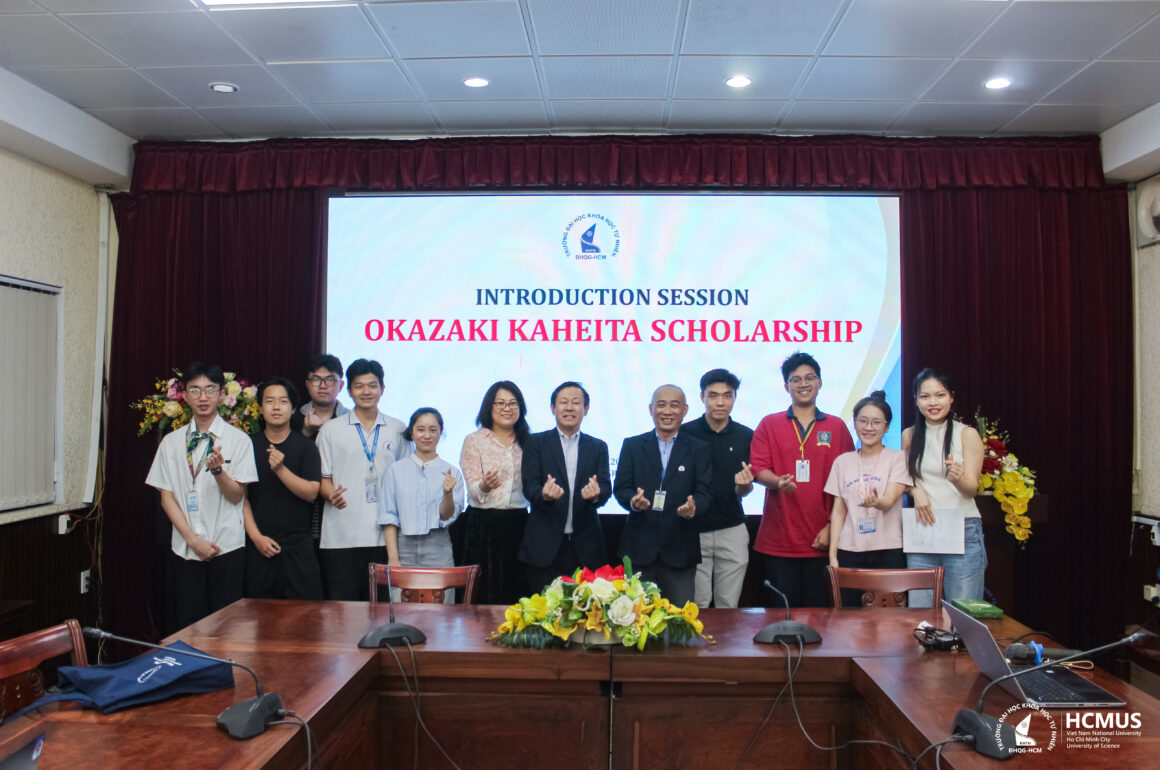
Chiều ngày 28/01/2026, Trường Đại học Khoa học tự nhiên, ĐHQG-HCM đã tiếp đón và làm việc với ông Takao Hisano – Giám đốc điều hành, đại diện Quỹ Học bổng Quốc tế Okazaki Kaheita (Nhật Bản), đến thăm và giới thiệu chương trình học bổng dành cho sinh viên Việt Nam có nguyện vọng theo học bậc thạc sĩ tại Nhật Bản. Tại buổi tiếp đón và làm việc, GS.TS Ngô Đại Nghiệp – Trưởng Phòng Quan hệ Đối ngoại Trường Đại học Khoa học tự nhiên, ĐHQG-HCM đã chủ trì trao đổi với đại diện Quỹ Okazaki. Tham...
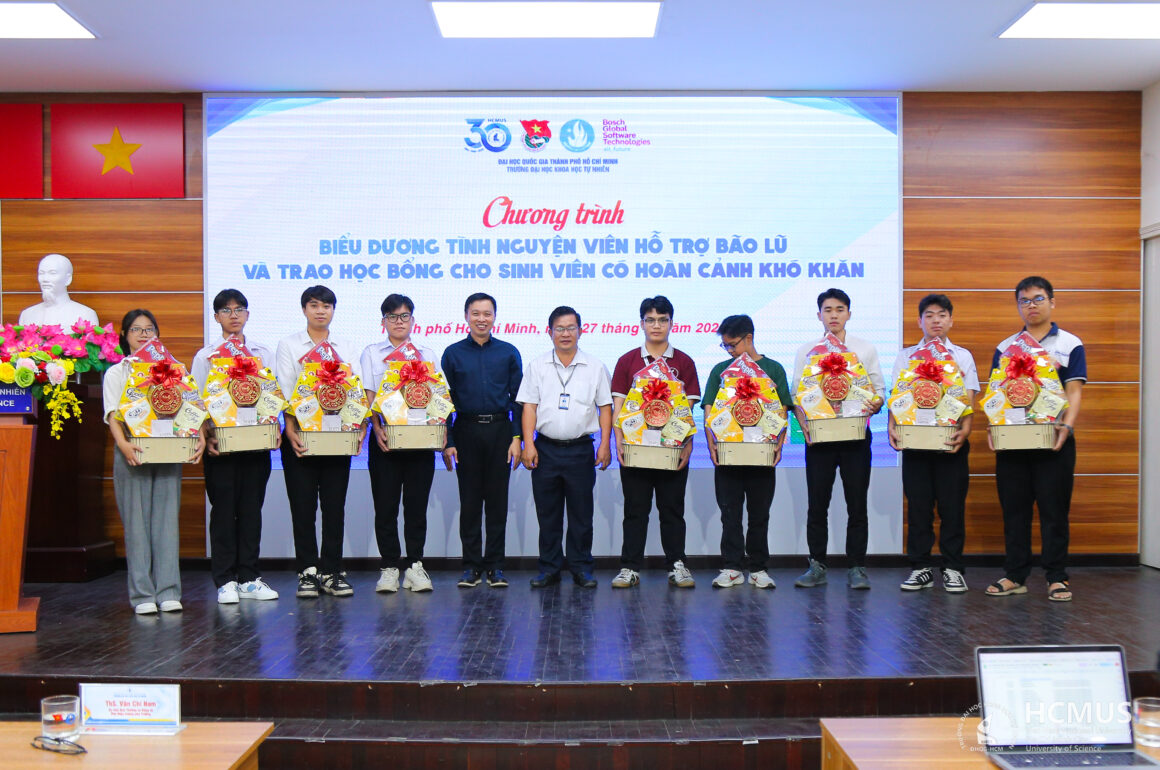

Biểu dương tình nguyện viên tham gia hỗ trợ đồng bào vùng lũ miền Trung và trao học bổng cho sinh viên khó khăn
Tối ngày 27/01, tại Trường Đại học Khoa học tự nhiên, ĐHQG-HCM (cơ sở Nguyễn Văn Cừ), Nhà trường đã tổ chức Chương trình Biểu dương lực lượng tham gia hỗ trợ đồng bào vùng lũ miền Trung, đồng thời trao học bổng cho sinh viên có hoàn cảnh khó khăn bị ảnh hưởng bởi thiên tai. Chương trình nhằm tổng kết các hoạt động hỗ trợ cộng đồng trong thời gian qua, ghi nhận những đóng góp thiết thực của cán bộ, viên chức, sinh viên và các đơn vị đồng hành. Trong bối cảnh các địa phương chịu...

Mời báo giá cung cấp Hàng hóa phục vụ cho đề tài nghiên cứu khoa học thuộc Sở Khoa học và Công nghệ tỉnh Đồng Nai
Kính gửi: Các hãng sản xuất, nhà cung cấp tại Việt Nam Hiện nay, Trường Đại học Khoa học tự nhiên, ĐHQG-HCM có nhu cầu tiếp nhận báo giá để tham khảo, xây dựng giá khái toán, làm cơ sở xây dựng giá các gói thầu, tổ chức lựa chọn nhà thầu Cung cấp hàng hóa phục vụ cho đề tài nghiên cứu khoa học thuộc Sở Khoa học và Công nghệ tỉnh Đồng Nai, nội dung cụ thể như sau: Thông tin báo giá: File đính kèm I. THÔNG TIN CỦA ĐƠN VỊ YÊU CẦU BÁO GIÁ: Yêu cầu...
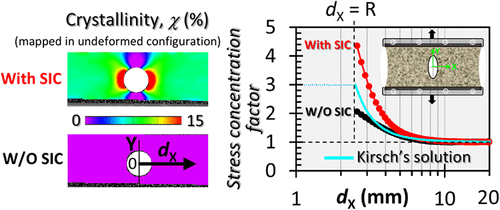
Coupled Evolution of Local Stress and Strain-Induced Crystallization Near a Circular Defect in Stretched Natural Rubber
Abstract We investigate the coupled evolution of heterogeneous strain, crystallinity, and stress fields in natural rubber (NR) sheets containing a circular hole during uniaxial stretching, with a focus on how strain-induced crystallization (SIC) influences local stress concentration at structural discontinuities. By high-resolution digital image correlation, an empirical strain-crystallinity relationship and a hyperelasticity analysis firmly grounded in stress–strain data obtained under diverse deformation modes, we quantitatvely map the spatial distributions of strain, SIC, and stress in the extreme vicinity (≈0.2 mm) of the defect. Local strain concentration at the lateral hole edges triggers pronounced SIC, resulting in strong stiffening and a...

Thông báo danh sách học viên cao học thuộc đối tượng tuyển thẳng, xét tuyển khóa 2023 được xét cấp học bổng đợt 2, năm thứ 2
THÔNG BÁO Danh sách học viên cao học thuộc đối tượng tuyển thẳng, xét tuyển khóa 2023 được xét cấp học bổng đợt 2, năm thứ 2 Căn cứ Quyết định số 1721/QĐ-KHTN ngày 07/09/2023 của Hiệu trưởng về việc ban hành Quy định cấp học bổng cho học viên thuộc diện tuyển thẳng và xét tuyển vào chương trình đào tạo trình độ thạc sĩ của Trường Đại học Khoa học tự nhiên, ĐHQG-HCM và Quy định kèm theo Quyết định này; Trường Đại học Khoa học tự nhiên thông báo danh sách học viên cao học thuộc...

“LỊCH SỬ DỤNG PHÒNG HỌP (Tuần 26/01/2026 đến 31/01/2026)”
Ngày Giờ Địa điểm Nội dung cuộc họp Đơn vị chuẩn bị Thành phần tham dự Thứ 2 26/01/2026 8:00 I 12 Bảo vệ luận văn thạc sĩ ngành Di truyền học Phòng ĐT SĐH Học viên cao học và thành viên hội đồng 9:00 I.11 Họp về điều chuyển tài sản của Trường Phổ Thông Năng Khiếu Phòng QTTB Phòng QTTB + Lãnh đạo, người phụ trách của Trường PTNK 14:00 F.102 Bảo vệ LATS cấp ĐVCM của NCS Phạm Thị Lợi, ngành Quản lý tài nguyên và môi trường Phòng ĐT SĐH NCS, HĐ, khách mời 14:00 I...

Thúc đẩy đăng ký và quản trị tài sản trí tuệ trong bối cảnh chuyển đổi số
Sáng ngày 26/01, tại Trường Đại học Khoa học tự nhiên, ĐHQG-HCM, Trung tâm Sở hữu trí tuệ và Chuyển giao công nghệ, ĐHQG-HCM (IPTC) đã phối hợp với Nhà trường tổ chức hội thảo “Đăng ký Sở hữu công nghiệp trong nước và quốc tế trực tuyến”. Hội thảo được tổ chức trong bối cảnh đẩy mạnh chuyển đổi số trong quản lý và khai thác tài sản trí tuệ, nhằm nâng cao hiệu quả đăng ký bảo hộ các kết quả nghiên cứu khoa học và đổi mới sáng tạo tại các cơ sở giáo dục đại học,...

NCS. Phan Ngọc Yến bảo vệ thành công luận án tiến sĩ cấp CSĐT ngành Đại số và Lý thuyết số
Ngày 14/01, tại Trường Đại học Khoa học tự nhiên, ĐHQG-HCM, nghiên cứu sinh Phan Ngọc Yến đã bảo vệ thành công luận án tiến sĩ cấp cơ sở đào tạo ngành Đại số và Lý thuyết số với đề tài “Hàm khoảng cách, bài toán tổng bình phương bé nhất và một số vấn đề liên quan”, dưới sự hướng dẫn khoa học của PGS.TS. Đinh Trung Hòa và TS. Nguyễn Anh Thi. Luận án tập trung nghiên cứu các vấn đề lý thuyết trong đại số, lý thuyết toán tử và phương trình ma trận, với định hướng...
![z5315371783557_8378ca28729a9f6b506dc8a7e766c5e2 [THÔNG BÁO] Học bổng Trung Quốc – Đông Nam Á](https://hcmus.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/z5315371783557_8378ca28729a9f6b506dc8a7e766c5e2-940x770.jpg)
[THÔNG BÁO] Học bổng Trung Quốc – Đông Nam Á
Phòng Quan hệ Đối ngoại xin chuyển thông tin từ ĐHQG-HCM về hai chương trình học bổng do Ban Thư ký Mạng lưới các Trường Đại học Đông Nam Á (ASEAN University Network – AUN) phối hợp với phía Trung Quốc triển khai cho năm học 2026–2027, cụ thể như sau: 1. Học bổng Trung Quốc – AUN năm học 2026–2027 (China–AUN Scholarship / Chinese Government Scholarship – AUN Programme): Đối tượng: Người đã tốt nghiệp đại học Bậc đào tạo: Thạc sĩ và Tiến sĩ Số lượng: 30 suất học bổng/năm Quyền lợi: Miễn học phí, chỗ ở, sinh hoạt phí...
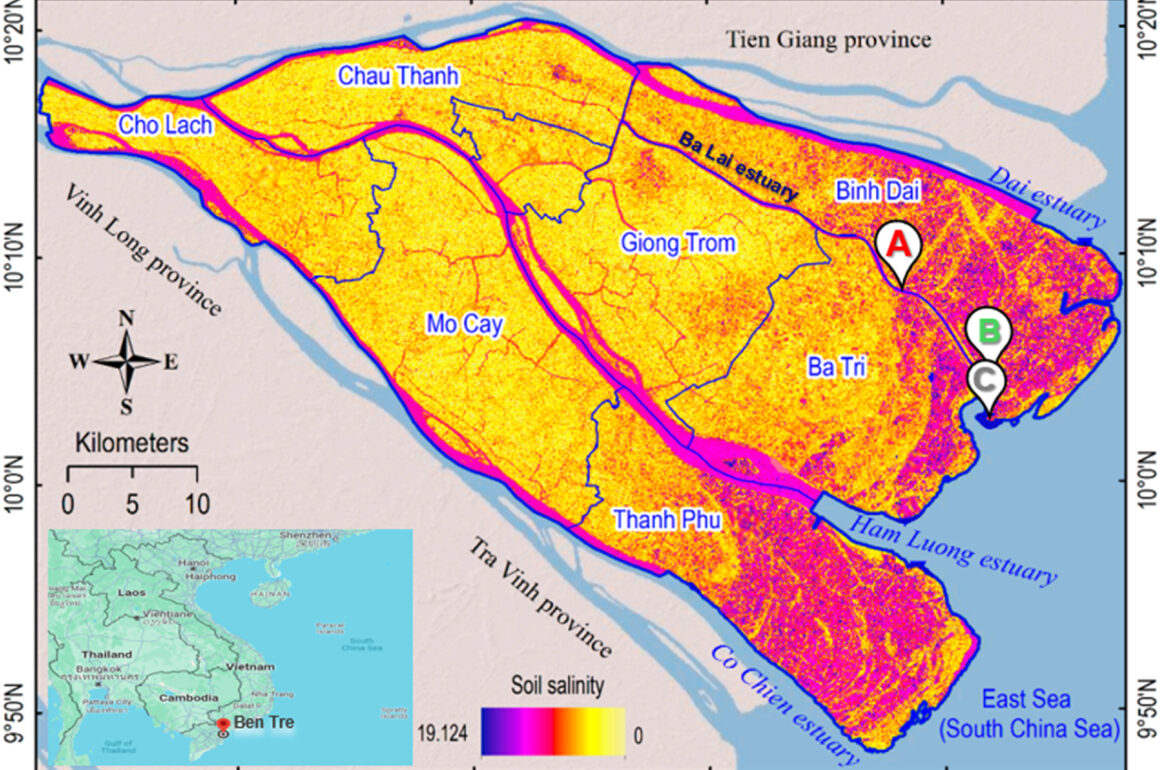
Hydrate technology for water desalination in the Mekong Delta, Viet Nam
Abstract Freshwater scarcity is a critical issue in Vietnam, particularly in the Mekong Delta, a densely populated region with an agriculture-based economy. This scarcity is largely driven by saltwater intrusion during the dry season, severely affecting both agriculture and the local economy. In response, advanced desalination technologies have been proposed. In this study, we investigated the use of cyclopentane (CP), a liquid guest molecule, and 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane (R134a), a gaseous guest molecule, as hydrate formers to desalinate saline water from the Mekong Delta. This study aimed to evaluate and compare the freshwater recovery efficiencies of these hydrate formers and assess the...


